Pardon our appearance
We are actively working to enhance your experience by translating more content. However, please be aware that the page you are about to visit has not yet been translated.
We appreciate your undertanding and patience as we continue to imporove our services.

Sustainability reporting has evolved from a niche concern into a central pillar of corporate strategy. As businesses face mounting expectations from regulators, investors, and customers, the ability to track and communicate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance is no longer optional. A sustainability reporting system offers a structured way to manage this responsibility, helping organizations stay accountable, transparent, and future-ready.
What Is a Sustainability Reporting System?
A sustainability reporting system is a digital platform or framework that helps organizations collect, analyze, and disclose ESG data. It’s designed to handle non-financial metrics, such as carbon emissions, energy usage, workforce diversity, and ethical sourcing, that reflect a company’s impact on the world.
These systems often integrate with existing enterprise tools to streamline data collection and ensure consistency across departments. They also support various reporting frameworks like GRI, SASB, and TCFD, helping companies as they navigate regulatory requirements and stakeholder expectations.
By centralizing ESG data, sustainability reporting systems enable businesses to move beyond ad hoc spreadsheets and manual tracking. They provide a reliable foundation for strategic decision-making, risk management, and public disclosures.
Key Takeaways
- Sustainability reporting systems can help companies align with global goals such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals or Net Zero targets. This alignment strengthens corporate purpose and guides long-term strategy.
- These systems offer clear, verifiable data that stakeholders can trust. Transparency builds credibility and fosters stronger relationships with investors, customers, and employees.
- By surfacing ESG risks early—such as supply chain vulnerabilities or regulatory gaps—companies can take proactive steps to avoid reputational damage and financial penalties.
- Real-time dashboards and analytics help leadership teams make informed decisions. Whether it’s optimizing energy use or improving diversity metrics, data-driven insights lead to smarter actions.
- Organizations with robust sustainability reporting often enjoy stronger brand loyalty and investor confidence. They may be better positioned to attract talent, secure funding, and lead in their industries.
Why Does Sustainability Reporting Matter?
Sustainability reporting is more than a compliance exercise—it’s a strategic asset. Governments around the world are tightening ESG disclosure requirements. In the European Union, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is reshaping how companies report non-financial data.
Beyond regulation, investors are increasingly factoring ESG performance into their decisions. They want to know how companies manage environmental risks, treat their workforce, and govern themselves. A transparent reporting system helps build trust and can improve access to capital.
Consumers also care. They’re choosing brands that reflect their values, and they expect companies to be honest about their sustainability efforts. A reporting system helps communicate those efforts clearly and credibly.
In short, sustainability reporting matters because it touches every part of the business—from compliance and finance to marketing and operations.
Key Features of an Effective Sustainability Reporting System
When evaluating sustainability reporting systems, it’s important to look beyond the surface. A good platform doesn’t just collect ESG data—it helps teams understand it, act on it, and communicate it effectively. The most valuable systems are those that support the full lifecycle of sustainability reporting, from data gathering and analysis to disclosure and stakeholder engagement. They should be built to handle complexity, scale with your organization, and adapt to changing regulatory demands.
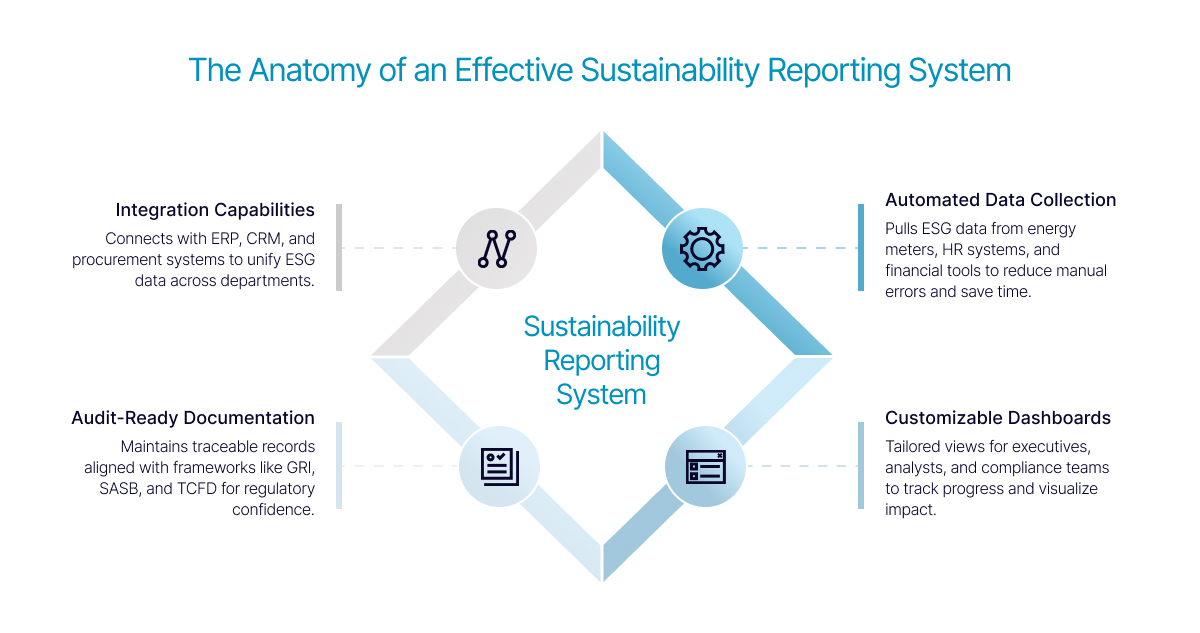
Automated Data Collection
Manual data entry is not only inefficient—it’s risky. Errors in ESG data can lead to compliance issues, reputational damage, and missed opportunities for improvement. Automated data collection solves this by pulling information directly from integrated sources such as energy meters, HR systems, procurement platforms, and financial tools. This ensures consistency and accuracy while freeing up time for teams to focus on analysis and strategy. Automation also supports continuous monitoring, which is increasingly important as companies move toward real-time reporting.
Customizable Dashboards
Sustainability data serves many audiences, from executives and board members to compliance officers and external stakeholders. A one-size-fits-all dashboard won’t cut it. Customizable dashboards allow users to tailor views based on their roles and priorities. For example, leadership may want a high-level snapshot of carbon emissions and diversity metrics, while ESG analysts need detailed breakdowns by region or business unit. These dashboards also make it easier to surface trends, track progress against goals, and communicate impact in a visually compelling way.
Audit-Ready Documentation
As ESG regulations become more stringent, the ability to produce audit-ready documentation is no longer optional. A strong reporting system maintains a clear trail of data sources, methodologies, and updates. It aligns with recognized frameworks like GRI, SASB, CDP, and TCFD, making it easier to respond to disclosure requirements and investor inquiries. Audit-ready systems also reduce the stress and cost of external reviews by ensuring that all documentation is organized, accessible, and verifiable.
Integration Capabilities
Sustainability doesn’t operate in isolation. It touches finance, operations, HR, procurement, and more. That’s why integration is critical. A reporting system should connect seamlessly with enterprise resource planning (ERP) tools, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and other internal systems. This creates a unified data environment where ESG metrics can be cross-referenced with financial performance, operational efficiency, and workforce trends. Integration also supports automation and reduces the need for manual reconciliation between systems.
Together, these features form the backbone of a sustainability reporting system that’s not just functional but transformative. They enable organizations to move beyond compliance and toward strategic sustainability leadership. When these capabilities are in place, reporting becomes a source of insight, alignment, and innovation rather than a box to check. Whether you're just starting your ESG journey or scaling an existing program, investing in a system with these features sets the foundation for long-term success.
How to Choose the Right Sustainability Reporting System
Choosing a sustainability reporting system is a strategic decision that can shape how your organization approaches ESG data, compliance, and stakeholder engagement. It’s not just about finding a tool that works today—it’s about selecting a platform that can evolve with your business, support your goals, and empower your teams. The right sustainability software should feel intuitive, scalable, and aligned with your internal workflows. Here are the key factors to consider when making your selection.
- Scalability: As your sustainability program grows, so will the complexity of your data and reporting requirements. Whether you're expanding into new markets, responding to emerging regulations, or adding new ESG metrics, your reporting system should be able to keep pace. Look for platforms that support multiple frameworks and offer flexible data architecture. This ensures you won’t need to switch systems as your needs evolve.
- User Experience: A system’s value depends on how easily people can use it. If the interface is clunky or confusing, adoption will suffer—even if the features are strong. The ideal platform should be intuitive enough for non-technical users while offering depth for ESG specialists. Clear navigation, visual dashboards, and contextual guidance all contribute to a better experience.
- Support & Training: Even the best systems require onboarding and ongoing support. Implementation can be complex, especially when integrating with existing tools or aligning with multiple reporting standards. Vendors that offer training resources, live support, and onboarding assistance can make a big difference in how quickly your team gets up to speed.
- Cost vs. Value: While cost is always a consideration, it shouldn’t be the only one. A lower-priced system may lack the flexibility, support, or compliance features you need. Instead, evaluate the long-term value: Will the system help you address risk, improve decision-making, and enhance your reputation? A slightly higher upfront investment can pay off in strategic benefits and operational efficiency.
Ultimately, the right sustainability reporting system should feel like a strategic partner—not just a piece of software. It should help your organization move from reactive reporting to proactive ESG leadership, supporting both day-to-day operations and long-term goals. When the system fits your needs and empowers your teams, sustainability becomes a shared responsibility and a source of innovation.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Sustainability reporting systems are actively shaping how organizations operate, communicate, and grow. Across industries, companies are using these platforms to improve transparency, respond to regulatory demands, and build stronger relationships with stakeholders. The impact is measurable, and the lessons are widely applicable.
For example, a supply chain company might use a sustainability reporting system to monitor emissions across its logistics network. By integrating ESG data with operational metrics, the company can identify inefficiencies, reduce fuel consumption, and improve vendor compliance. These insights not only support environmental goals but could also lead to cost savings and stronger supplier relationships.
A technology firm could adopt real-time sustainability reporting to monitor its energy usage across data centers. With continuous updates, the company can respond quickly to spikes in consumption, adjust operations, and share progress with stakeholders. This level of transparency helps build trust and demonstrates accountability.
A mid-sized manufacturer might use a reporting system to align with new ESG regulations. By centralizing data from HR, procurement, and operations, the company can produce audit-ready reports in response to disclosure requirements. This not only supports compliance but also positions the company as a responsible player in its industry.
Even a regional service provider can benefit from sustainability reporting. By tracking workforce diversity, community engagement, and energy efficiency, the organization can better understand its social and environmental impact. These insights can inform hiring practices, community partnerships, and operational improvements.
When companies treat ESG data as a strategic asset, they gain insights that drive innovation, efficiency, and resilience.

Common Sustainability Reporting Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Implementing a sustainability reporting system can be transformative, but it’s not without its hurdles. Organizations often face internal resistance, technical limitations, and evolving compliance demands. The good news is that these challenges are manageable—and the right platform can make a significant difference in how smoothly the transition goes. Below are some of the most common obstacles and practical ways to overcome them.
Data Silos
One of the biggest barriers to effective sustainability reporting is fragmented data. ESG metrics often live in separate systems across departments, finance, HR, operations, procurement, and pulling them together can be time-consuming and error-prone. Breaking down these silos requires both cultural and technical solutions. Internally, teams need to align on shared goals and reporting standards. Technically, the reporting system should support integrations that unify data sources and automate collection.
Lack of Expertise
Not every organization has a dedicated sustainability team, and ESG reporting can be complex. From understanding frameworks to interpreting metrics, the learning curve can be steep. To overcome this, companies can invest in training, hire consultants, or choose platforms that offer built-in guidance. A system that simplifies workflows and provides contextual help can empower non-experts to contribute meaningfully.
Changing Regulations
The ESG landscape is constantly evolving. New disclosure rules, shifting stakeholder expectations, and emerging frameworks can make it difficult to navigate compliance. Companies need systems that are flexible and regularly updated to reflect regulatory changes. Subscribing to ESG news, joining industry groups, and working with vendors who monitor compliance trends can help organizations stay ahead.
Stakeholder Alignment
Different stakeholders often have different priorities. Executives may focus on strategic outcomes, while compliance teams are concerned with accuracy and auditability. Balancing these needs requires a system that can present data in multiple formats and levels of detail. Clear communication and customizable dashboards help ensure everyone gets the insights they need.
Facing these challenges head-on is part of building a resilient and forward-looking sustainability program. With the right tools and a thoughtful approach, organizations can turn obstacles into opportunities—streamlining operations, improving transparency, and strengthening stakeholder trust.
The Future of Sustainability Reporting
Sustainability reporting is evolving rapidly. What began as a compliance-driven exercise is now becoming a dynamic, strategic function within organizations. As technology advances and stakeholder expectations grow, reporting systems are adapting to offer deeper insights, faster updates, and more transparent communication. The future of sustainability reporting will be shaped by innovation, integration, and a stronger emphasis on accountability.
Real-Time Reporting
Annual ESG reports are giving way to more frequent updates. Real-time reporting allows organizations to share progress as it happens, respond quickly to stakeholder inquiries, and make timely adjustments to their strategies. This shift supports greater transparency and agility, especially in industries where sustainability metrics change rapidly.
Nasdaq Metrio™ enables real-time data tracking and campaign management, allowing teams to monitor ESG metrics continuously and communicate updates through customizable dashboards.
Traceability and Data Integrity
As sustainability reporting becomes more sophisticated, traceability emerges as a critical capability. Organizations need to verify the origin, accuracy, and completeness of their ESG data—especially when it comes to supply chain disclosures, emissions tracking, and social impact metrics. Traceability ensures that data can be followed back to its source, validated, and confidently shared with stakeholders.
This is particularly important for companies that rely on third-party vendors or global operations, where ESG risks may be harder to monitor. A strong reporting system should offer clear audit trails, version histories, and documentation workflows that support data integrity and accountability.
Nasdaq Metrio helps organizations manage traceable ESG data through built-in audit trails, campaign tracking, and documentation tools that align with evolving standards. These features make it easier to verify inputs, respond to stakeholder inquiries, and maintain confidence in reported outcomes.
Stakeholder-Centric Design
As ESG reporting becomes more public-facing, systems will need to support storytelling and engagement. This means offering tools that help organizations communicate their impact clearly and credibly—whether through interactive dashboards, infographics, or narrative summaries. The goal is to make sustainability data accessible and meaningful to a wide range of audiences.
Nasdaq Metrio supports stakeholder engagement through its customizable dashboards, visual storytelling features, and role-based access controls that tailor content to different user groups.
The future of sustainability reporting is about more than technology—it’s about building trust, driving action, and embedding ESG into the core of business strategy. As systems become smarter and more integrated, organizations will be better equipped to lead with purpose and deliver measurable impact.
Why Nasdaq Metrio Stands Out
For organizations exploring sustainability reporting platforms, Nasdaq Metrio offers a compelling set of features designed to support both foundational and advanced ESG programs. Its platform is built to scale with growing data needs, align with global reporting frameworks, and simplify the complexities of sustainability disclosure.
Nasdaq Metrio supports automated data collection through integrations and bulk uploads, helping teams reduce manual effort and improve accuracy. Its customizable dashboards allow users to tailor insights for different audiences—from executives to compliance teams—making ESG data more accessible and actionable. The platform also includes audit-ready documentation tools, with built-in support for over 15 ESG frameworks, helping organizations stay aligned with evolving regulations.
Beyond technical capabilities, Nasdaq Metrio emphasizes usability and support. Its clean interface, in-platform guidance, and access to ESG specialists make it approachable for teams at any level of expertise. Whether you're just starting your sustainability journey or looking to enhance an existing program, Nasdaq Metrio is designed to help organizations turn ESG data into strategic insight.

Sustainability reporting has moved from the margins to the center of business strategy. As expectations rise—from regulators, investors, customers, and employees—organizations need systems that do more than just collect data. They need platforms that help them understand their impact, communicate it clearly, and make informed decisions that align with long-term goals.
Choosing the right sustainability reporting system is about more than checking boxes. It’s about finding a solution that fits your organization’s size, complexity, and ambition. The best systems offer automation, flexibility, and traceability, while also supporting collaboration across departments and transparency with stakeholders.
As reporting evolves toward real-time insights, predictive analytics, and deeper stakeholder engagement, companies that invest in robust, scalable platforms will be better positioned to lead. Whether you're just starting your ESG journey or refining a mature program, the tools you choose today will shape your ability to respond to tomorrow’s challenges.
Sustainability is no longer a side initiative—it’s a lens through which every business decision is viewed. With the right reporting system in place, organizations can turn ESG data into a source of clarity, accountability, and competitive advantage.
Sustainability Reporting System FAQs
Is sustainability reporting mandatory for all companies?
Not universally, but regulations are expanding. In many regions, large companies are already required to disclose ESG data, and smaller organizations may soon be included. Even where reporting isn’t mandatory, voluntary disclosure is increasingly expected by investors and customers.
What frameworks should be used for sustainability reporting?
The most widely used frameworks include GRI (Global Reporting Initiative), SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board), TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures), and CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project). The right framework depends on your industry, stakeholder expectations, and regulatory environment. Many companies use a combination to meet different needs.
Can small and mid-sized businesses benefit from sustainability reporting?
Absolutely. Even basic reporting can help build trust, attract investment, and prepare for future regulations. It also supports internal decision-making by highlighting areas for operational improvement and risk reduction.
How often should sustainability reports be updated?
Annual reporting is common, but many organizations are moving toward quarterly updates or real-time dashboards—especially for climate-related metrics. The frequency should reflect your stakeholders’ expectations and the pace of change in your ESG data.
What’s the difference between ESG reporting and sustainability reporting?
ESG reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance metrics that are material to investors. Sustainability reporting is broader and may include additional topics like community engagement, ethical sourcing, and long-term impact. The two often overlap, but they serve slightly different audiences and purposes.
How do you know if a reporting system is right for your organization?
Look for platforms that align with your size, goals, and technical capacity. Key features to consider include automation, scalability, integration with existing systems, support for multiple frameworks, and ease of use. A good system should help you move from compliance to strategic insight.
What kind of support should be expected from a reporting system vendor?
Ideally, vendors should offer onboarding assistance, training resources, live support, and regular updates to reflect changing regulations. Some platforms also provide access to ESG specialists who can help guide your reporting strategy.
